Mandible
The mandible is a bone of the lower face which includes the entire lower jaw, lower dental arch and teeth. Parts of the mandible include the chin, the base of the mandible and the ramus. A large, heavily developed mandible is an important feature of masculine faces. Heavily developed mandibles are broad and include projecting chins and long ramuses. Ramus length is affected by testosterone levels.[1]
People with maxillary retrusion tend to have weakly developed mandibles—narrow palates, obtuse gonial angles, short base of mandible, and receding chins, which creates a weak appearance to the face.
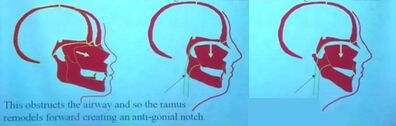
A retruded or downward ramus will obstruct the airway. To compensate for the airway obstruction, the bottom of the ramus shifts forward. This will result in an increased gonial angle, which is a detriment to aesthetics.
Ramus length is more affected by testosterone rather than maxillary retrusion. However, a retruded maxilla will make the ramus appear less vertical, making it appear shorter as a result.
See also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Verdonck, A., Gaethofs, M., Carels, C., & de Zegher, F. (1999). Effect of low-dose testosterone treatment on craniofacial growth in boys with delayed puberty. The European Journal of Orthodontics, 21(2), 137-143.