Mentalcel
A mentalcel refers to individuals whose inceldom is due to psychological factors. This includes conditions like depression, autism spectrum disorders (Asperger's Syndrome), schizophrenia, dementia, PTSD, ADHD, AVPD, schizotypal disorder, Cluster A personality disorders, body dysmorphic disorder, severe anxiety disorders (notably social anxiety), and overall neuroticism.
Causes[edit | edit source]
Some mentalcels attribute their situation as deriving from non-DSM related issues such as being misanthropic, alexithymic, hedonophobic, cherophobic, or a strictly allosexual aromantic. Some mentalcels either turn to ascetism or languish in dreephilia. Among heterosexual women, mentalceldom sometimes derives from phallophobia, and among hetero men, it may derive from eurotophobia. Mentalcel is a hyponym of the word medcel.
Although many incels (particularly blackpilled incels) are prone to consider those who attribute their sexlessness primarily to mental health issues to be fakecels, there is a plethora of evidence that suggests that mental health status is one of the strongest determinates of ones' sexual market value and overall mating behaviours.
For instance, people with certain psychiatric conditions are far less likely to reproduce, be married or be sexually successful than probands of a similar age and sex, with massive effect sizes in this regard found for autism spectrum disorders and schizophrenia, and large effects found for social anxiety disorders (among men), with these conditions seemingly the most harmful in terms of hampering one's sexual and relationship success. The substantial assortative mating (birds of a feather flocking together) effects found among those relative few who do manage to reproduce or find a partner, also indicates that people strongly take others mental health status into account when selecting a mate.[1]
There is also plentiful evidence that mentalceldom is particularly harmful to men's sexual success, with evidence that men with mental health concerns are twice as likely than women with mental health concerns to go sexless, together with it being found that several psychiatric conditions are much more harmful to male sufferer's relationship success and achieved fertility throughout a lifespan than female sufferers.[2][3][4]
"Normal" mentalcels[edit | edit source]
Although the term mentalcel seems to imply a neurological disorder, preventing a romantic relationship, the scope of mentalceldom also includes totally normal men. Several studies have found that psychopathic men are more attractive to women than non-psychopathic men.[5] This brings the topic of mentalceldom into a grey area. Who is actually crazy? Is the normal guy whose normalness renders him boring to women crazy? Or is the psychopathic male harmful to society, but nonetheless endearing to women crazy? Yes, the normal guy whose normalness is boring is crazy, but society would have us believe otherwise. Psychopathic traits have flourished in society because those biological traits have proven to result in higher fertility.
Even women who adamantly claim that they oppose psychopathic traits, actually find psychopaths a turn-on and will freely admit to preferring a man whom is very assertive. The man should be leading the romantic interactions and liaisons. This demand for assertiveness would have been a reasonable demand in the 1930s, and earlier when most of the cards were in the man's hands. But are these demands still reasonable in the 21st century when many of those cards are in women's hands? Women match or outmatch men at adulting in several ways for example they leave the home earlier, they're more likely to have a university degree, they are also more likely to have first-hand experience growing up with an adult parent of the same sex, and therefore much higher access to mentorship and a role model (see momad syndrome for how mother-son mentorship is fraught with inexpedience). All these factors and more means power has shifted into the hands of women. Women are aware that the cards are in their hands but simply try to find men that hold even more cards than they do.
How often do women say "He's just not sufficiently cool, funny, entertaining, or dangerous enough"? Is it really necessary for a man to have these qualities, why can't a man simply be normal, or bland? The answer is of course that normal men have lower fertility. This situation has blurred the line between what constitutes a mentalcel and doesn't. A guy could have straight A's at school, be neurotypical, and therefore slightly less assertive than the other guy and as such get disqualified as a mate. In the modern dating scene something as simple as being unassertive relegates men into the mentalcel camp. In laymen's terms, being mentally normal, renders a man mentally defective.
Nurture vs nature[edit | edit source]
Nurture vs nature is a debate on the development of one's phenotype. Academic fields wherein this debate occurs includes ecology, behavioural genetics, epigenetics and social determinism. The introductory paragraph largely focuses focused on psychological problems which can often be attributed to nature. On the other hand, mentalceldom can also be a by-product of upbringing. This is called nurture.
Mentalcels have often grown up in a helicopter parenting household, a state that often results in hedonophobia, which inhibits people from seeking what they want. Mentalcels who had an abusive upbringing are sometimes called PTSDcels or abusecels. A great skit showcasing the mentalcel trajectory was made by Buzzfeed in a video called "Beta Male".[6]
Other nurture-based factors that have been suggested as contributing to mentalceldom include schooling in single-sex rather than coed or mixed-sex education. However, all the aforementioend points are difficult for many people to accept, partially because of the following black pill: some parents just don’t love their children.
Life History and the Autism-Psychosis Spectrum[edit | edit source]
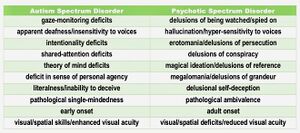
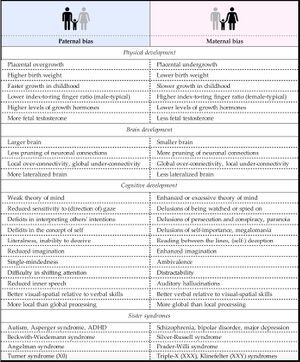
Scott Alexander, a psychiatrist, noted[7] that there is an axis independent from the wellness-illness axis, for subclasses of mental illness, where Autists and ADHD are on one end and Psychosis is on the other. This is called the Imprinted Brain Theory[8][9][10][11]. Genetic analysis cluster confirms that there are four major clusters[12], and symptoms of negative schizotypy mirrors Autism[13][14], Machiavellianism and lack of Narcissism[15], which is orthogonal to positive schizotypy (social difficulty and disorganization), which closer approximates psychopathy[15]. However, academia has been considering Asperger's to be misclassed version of developmental psychosis, rather than Autism[16][17], since they are more feminized than Low Functioning Autists[18]. It is possible that faux autists and bipolars are generally fast LH and are more masculinized (similar to Psychopathy), whilst real autists are slow LH and are more feminized (similar to Machiavellianism and anti-Narcissism). This can also be related to female masculinization[19] and age of birth[20] (Autists have older dads and parents in general, Schizos have younger dads and mom who hit The Wall).
There are evidence[21] that suggests that cognitive genetics are correlated to autism, that cognitive and non-cognitive genetics are correlated to slow LH, neighborhood integration, Openness, and Emotional Stability (implying intelligence), that non-cognitive genetics are correlated to health, and that non-cognitive genetics that goes against cognition are correlated to risk tolerance, bipolar, schizophrenia, Conscientiousness, Agreeableness, and Extraversion (implying social adaptiveness is related to Psychopathy).
Paradox of Looks and Mentalcels[edit | edit source]
Problem with this model however, is that if autism is caused by paternal bias, and are more masculinized and machiavellian face. However females are more likely to be attracted to a psychopathic face, rather than a face of an autist or machiavellian, which implies they are attracted to feminized faces by proxy.
There are three major axis of facial traits[22][23][24]: Dominance, Approachability, and Youthfulness. These dimensions are disputed[25] however. Correlation[26][27] between viewed personality and these dimensions can be derived, but females can only accurately predict Openness (being approachable), Extraversion (being older and approachable), and Agreeableness (being older, approachable and non-dominant), where the first factor relates to intelligence, and the other two relates to psychopathy-like traits, which implies aged dominance has an effect on psychopathic attractiveness, which is orthogonal to merit-like traits.
A further reduction of this model into two dimensions can be done[28][29] as masculinity/dominance/attraction (lack of cognitive ability as hinderance), and femininity/approachability/friendliness (non-cognitive ability).
Extension to Psuedo-Astrology[edit | edit source]
It is known[30] that Schizophrenics are most likely to be born in either February or March, compared to August or September. The same can be said[31] for Autism, October and November, compared to April and May. For Depression[32], June and July, compared to December and January.
Middle-aged mentalceldom[edit | edit source]
See the adult degenitalization section of tricenarian for how a prudish upbringing can haunt someone well into their adult years.
Androphobia[edit | edit source]
Mentalceldom is sometimes caused by internalized androphobia. Being raised as a boy in an otherwise all-female household that championed feminism is the most likely culprit of internalized androphobia, especially if at least one of these female relatives has a combination of social anxiety disorder as well as narcissistic disorder. The reason why internalized androphobia can cause mentalceldom is for the same reason that androphobia in women can hamper their changes at relationships. Its because you stumble and falter at courtship, even though courtship should be the most natural thing in the world as it perches from millions of years of evolution. Whereas in women androphobia recognized all men as potential threats, internalized androphobia turns that fear inwards and men become overly self-conscious whereby they view themselves as a menace-in-waiting when around the opposite sex.
Mental health[edit | edit source]
Involuntary celibacy has been attributed to psychological factors, such as social awkwardness, a lack of social skills,[33] lack of confidence or flirting skills, trust issues, addiction,[34] shyness,[35] recreational sex invoking feelings of guilt, fears of unreciprocation of romantic overtures or apathy[36] or an inability to decipher social cues.[37] It has also been suggested that people who live involuntarily celibate lives may have psychological disorders such as depression, Asperger syndrome, and body dysmorphic disorder.[38]
The "therapy" interjection[edit | edit source]
It has also been suggested that there is a correlation between involuntary celibacy and other psychological issues such as neuroticism, anxiety, and autism, extreme introversion or general mental ailments. Ie. unattractive personality disorders.[39]
One of the most common interjections made by bluepilled normies when coming across a mentalcel is along the lines of "go seek therapy". But what these normies fail to realize is that the training received by modern western therapists isn't exactly tailor-made for men. For example, it remains difficult for modern therapists to fathom that abuse can be female perpetrated, especially when its female-against-male, due to a systemic and gynocentric system that nauseates at the thought of depicting women in an unflattering light. As such, one of the main culprits of mentalcel dysfunctionality at the home, the single mother's emotional and psychological abusiveness, remains unviable territory for therapists.
Interview[edit | edit source]
Women's attraction to cluster B personality disorders are so strong, this man was able to become a reproductive success despite being an autistic, hi IQ, turbo manlet. The woman in the video also has cluster B personality disorders, thus the two are assortatively mated, for dark triad traits. Their son is on the autism spectrum, and has hi IQ.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/article-abstract/2494707
- ↑ https://incels.wiki/w/Scientific_Blackpill#Mental_disorders_significantly_reduce_male_fertility.2C_substantially_more_than_they_do_for_women
- ↑ https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/article-abstract/2494707
- ↑ https://www.medscape.org/viewarticle/482059_3
- ↑ https://www.local10.com/health/study-claims-psychopathic-traits-of-men-more-attractive-to-women
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Zr5qzV-8Zkc
- ↑ https://astralcodexten.substack.com/p/ontology-of-psychiatric-conditions-653
- ↑ https://www.wikiwand.com/en/Imprinted_brain_hypothesis
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020116
- ↑ https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/the-imprinted-brain/201901/the-imprinted-brain-theory-in-thousand-words
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2014.0604
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.22.20196089
- ↑ https://primate.uchicago.edu/2014EHB.pdf
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063316
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 https://doi.org/10.1177/0033294117742655
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.13599
- ↑ http://www.sfu.ca/biology/faculty/crespi/pdfs/CrespiRitsner2010.pdf
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11263685
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1111/eva.13244
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1093/emph/eow023
- ↑ https://archive.ph/vJcjH
- ↑ https://www.marianosardon.com.ar/verbal/verbal_stuff/sutherland.pdf
- ↑ http://bishoplab.berkeley.edu/multifeatmodeling.html
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107721
- ↑ https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-25500-y
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01616
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01616
- ↑ https://digitalrepository.unm.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1037&context=biol_etds
- ↑ https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1364661305003207
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199902253400803
- ↑ https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/54153
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssmph.2018.03.008
- ↑ https://news.vice.com/en_us/article/7xqw3g/this-is-what-the-life-of-an-incel-looks-like
- ↑ https://www.newshub.co.nz/home/lifestyle/2018/08/the-science-of-incels-all-the-reasons-why-some-men-can-t-find-a-partner.html
- ↑ http://www2.gsu.edu/~wwwexa/news/archive/2001/01_0724-invcelrel.htm
- ↑ https://www.foxnews.com/story/foxsexpert-5-ways-to-fix-a-sexless-marriage
- ↑ https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/minority-report/201706/involuntary-celibacy
- ↑ https://www.newstatesman.com/2018/05/we-must-try-understand-how-unwanted-virginity-leads-self-hating-incels-murder
- ↑ Dewey, Caitlin (October 7, 2015). "Incels, 4chan and the Beta Uprising: making sense of one of the Internet's most-reviled subcultures". The Washington Post.
See also[edit | edit source]
Well-known incel categories
| Origin & race |
Arabcel • Beancel • Blackcel • Currycel • Ethnicel • Francel • Hapacel • Italiancel • Slavcel • Persocel • Redcel • Ricecel • Turkcel • Whitecel |
|---|---|
| Religion | |
| Disease & mental |
Mentalcel • Autistcel • Spergcel • Disabledcel • Emcel • Gynocel • Manchildcel • Medcel • PSSDcel • Stuttercel • Downcel |
| Looks |
Acnecel • Baldcel • Chincel • Cutecel • Dickcel • Eyecel • Fatcel • Framecel • Haircel • Heightcel • Nosecel • Ramuscel • Thincel • Uglycel • Wristcel • Earcel • Gingercel |
| Sex |
Mancel • Femcel-lite • Femcel • Truefemcel • Lesbocel • Queercel • Rainbowcel • Transcel • Intercel • Kinkcel |
| Job | |
| Misc. |
Cybercel • Escortcel • Incompetencel • Gymcel • Locationcel • Countrysidecel • Denialcel • Nearcel • Semicel • Noncel • Fakecel • Truecel • Volcel • Nymphocel • Marcel • Mismatchcel • Oldcel • Youngcel • Shycel • Incelosphere rifts • Standardcel • Stoicel • Voicecel • Weebcel • Sistercel • Protocel • StormFrontcel • Kitchencel • Happycel • Tiktokcel |